41 r factor levels labels
Getting Started with R - Part 7: Factors - Levels and Labels Changing levels. You can set the levels labels after constructing a factor. This would be similar to passing in the labels parameter. We can pass a full new vector or just labels the labels of the levels selectively. Let us just change factor label 1 from "Jack" to "Mr. Prelutsky". 如何理解R中因子(factor)的概念? - 知乎 labels:设置各水平名称 (前缀) ,与水平一一对应; ordered:设置是否对因子水平排序,默认 FALSE 为无序因子, TRUE 为有序因子; 该函数还包含参数 exclude:指定有哪些水平是不需要的 (设为NA) ;nmax 设定水平数的上限。 若不指定参数levels,则因子水平默认按字母 ...
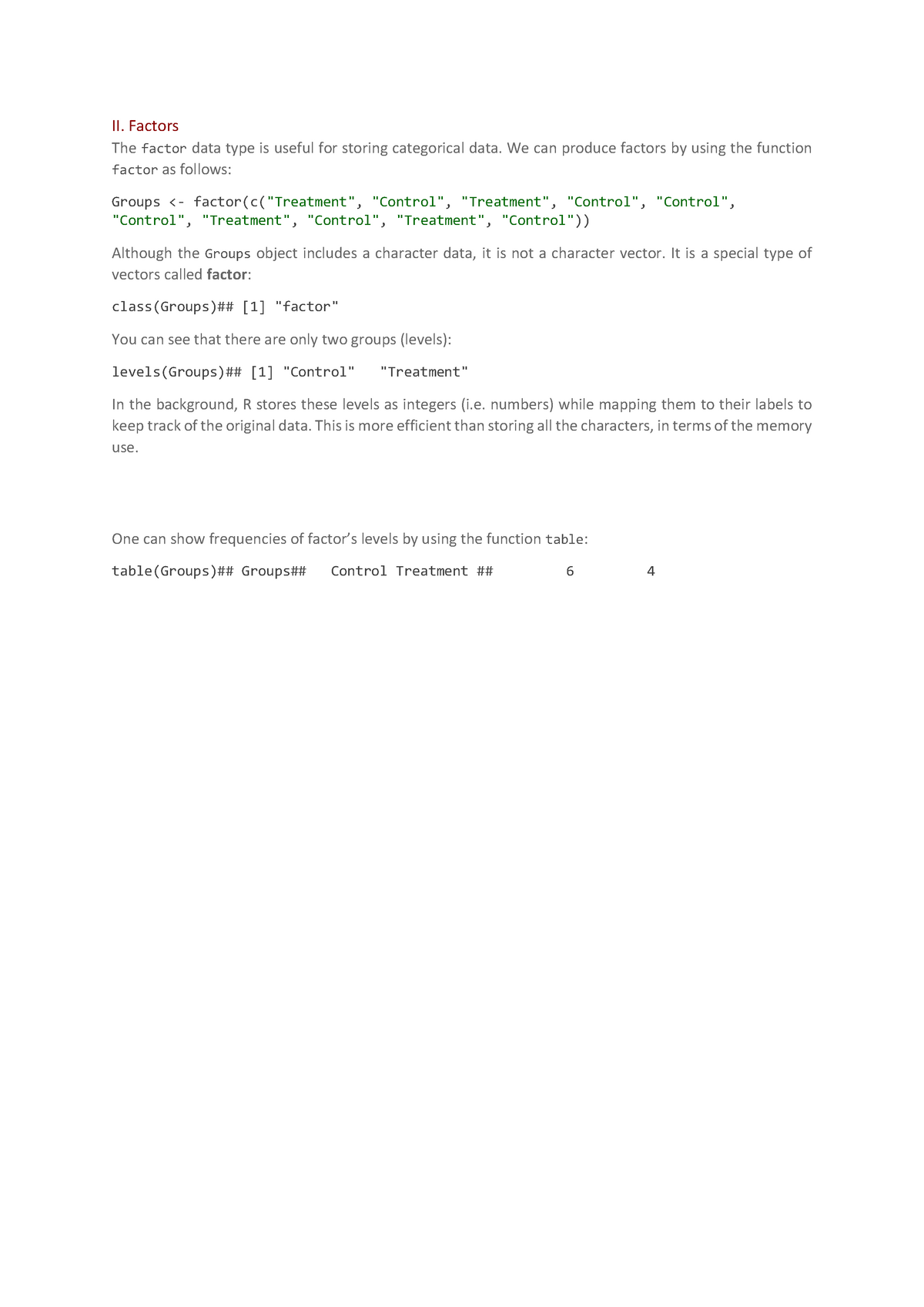
R 因子 | 菜鸟教程 R 因子 因子用于存储不同类别的数据类型,例如人的性别有男和女两个类别,年龄来分可以有未成年人和成年人。 R 语言创建因子使用 factor() 函数,向量作为输入参数。 factor() 函数语法格式: factor(x = character(), levels, labels = levels, exclude = NA, ordered = is.ordered(x), nmax = NA) 参数说明: ..

R factor levels labels
r - Why is the terminology of labels and levels in factors so weird ... Another way to think about levels is that factor(x,levels=L1,labels=L2) is equivalent to. f <- factor(x,levels=L1) levels(f) <- L2 I think an appropriately phrased version of this example might be nice for Pat Burns's R inferno-- there are plenty of factor puzzles in section 8.2, but not this particular one ... Levels in R: What are the Factor Levels - R-Lang The levels () is an inbuilt R function that provides access to the levels attribute. The first form returns the value of the levels of its argument, and the second sets the attribute. You can assign the individual levels using the gl () function. When you first get a dataset, you will usually notice that it contains particular factor levels. An Introduction to R However in this simple instance (just one factor) what happens can be thought of as follows. The values in the vector are collected into groups corresponding to the distinct entries in the factor. The function is then applied to each of these groups individually. The value is a vector of function results, labelled by the levels attribute of the ...
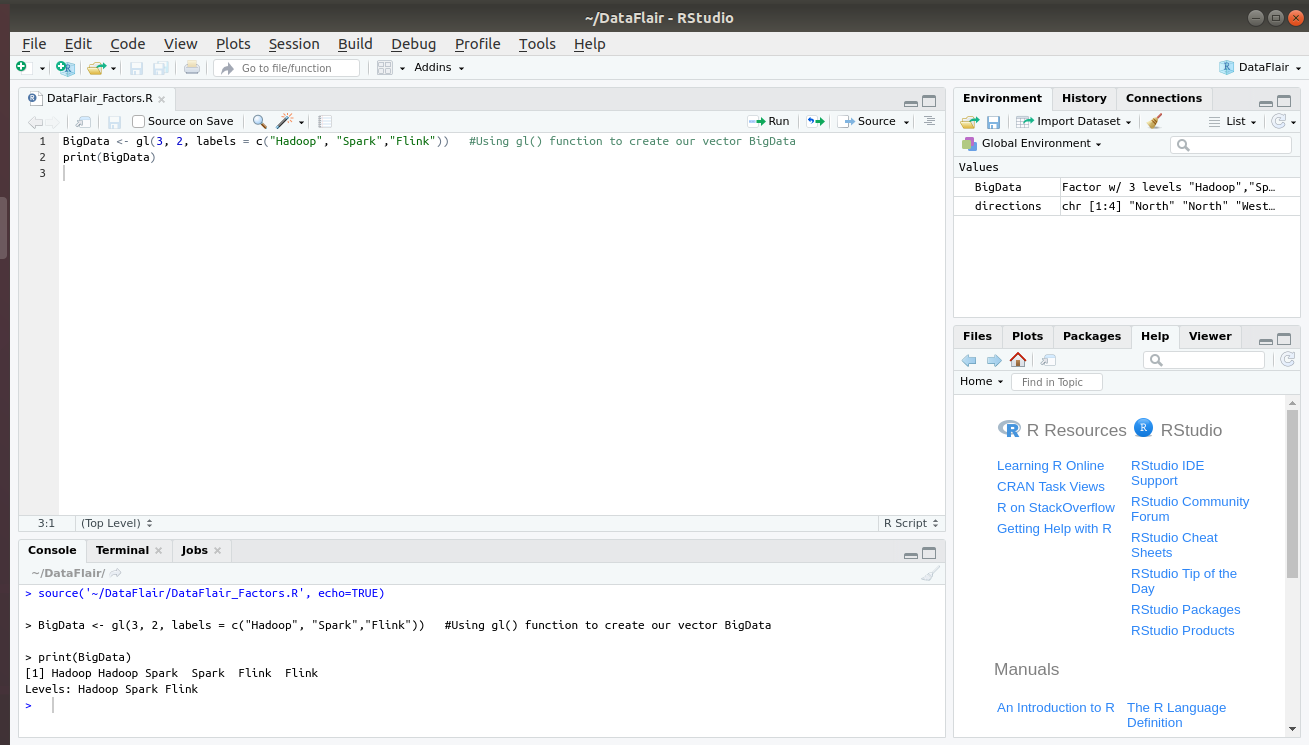
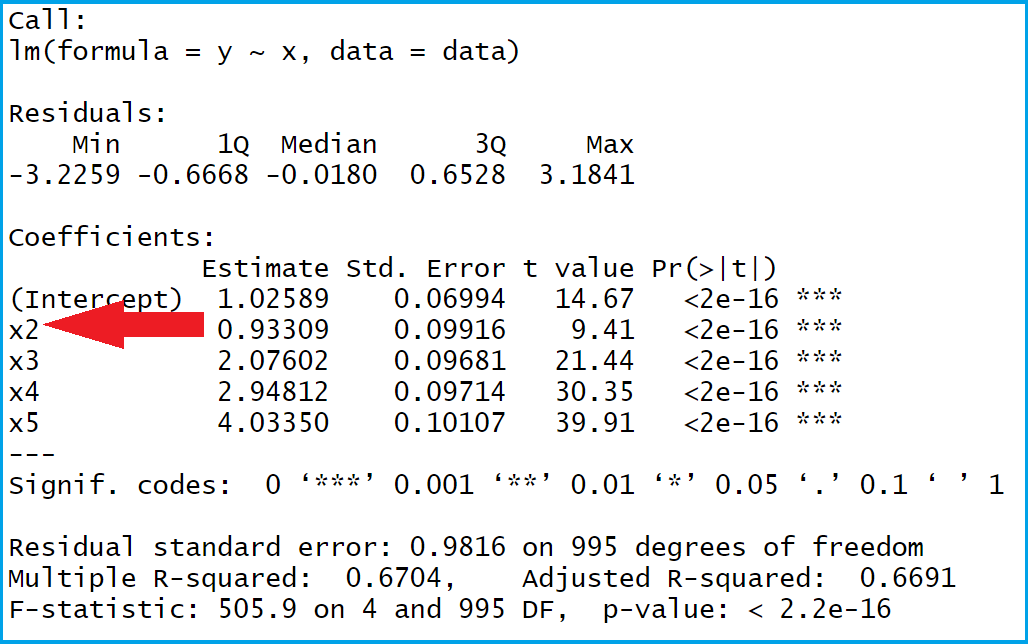
R factor levels labels. R Factor and Factor Levels: How to Create Factors in R - R-Lang How to Create Factor in R. To create a Factor in R, use the factor () method. The factor () method takes a vector as an input and returns the factor. The factor () function is used to encode a vector as a factor. If the argument ordered is TRUE, the factor levels are considered to be ordered. For compatibility with S, there is also a function ... Factor Levels in R | DataCamp R allows you to do this with the function levels (): levels (factor_vector) <- c ("name1", "name2",...) A good illustration is the raw data that is provided to you by a survey. A common question for every questionnaire is the sex of the respondent. Here, for simplicity, just two categories were recorded, "M" and "F". How to Generate Factor Levels in R using gl() Function - R-Lang Generate Factor Levels in R. To generate factor levels in R, use the gl() function. The gl() function produces the factors by defining the pattern of their levels. ... It is an optional vector of labels for the resulting factor levels. ordered: It is a logical argument indicating whether the result should be ordered or not. Example. sv <- gl(3 ... r - `lm` summary not display all factor levels - Stack Overflow Switching the order of the call so that + F - 1 precedes + B - 1 results in coefficients of all levels of F being visible but not B1. Does anybody know either how to display all levels of both B and F, or how to assess the relative weight of F1 compared to other levels of F from the outputs I have?
r - Cleaning up factor levels (collapsing multiple levels/labels ... Haven't tested this yet, but the R 3.5.0 (2018-04-23) release notes say "factor(x, levels, labels) now allows duplicated labels (not duplicated levels!). Hence you can map different values of x to the same level directly." - Aaron left Stack Overflow. Apr 26, 2018 at 4:51. How to Reorder Factor Levels in R (With Examples) - Statology Occasionally you may want to re-order the levels of some factor variable in R. Fortunately this is easy to do using the following syntax: factor_variable <- factor (factor_variable, levels =c(' this ', ' that ', ' those ', ...)) The following example show how to use this function in practice. Vitamin D - Health Professional Fact Sheet The labels must list vitamin D content in mcg per serving and have the option of also listing the amount in IUs in parentheses. Foods providing 20% or more of the DV are considered to be high sources of a nutrient, but foods providing lower percentages of the DV also contribute to a healthful diet. ** Vitamin D is in the yolk. R Factors - Operating on Factors and Factor Levels - TechVidvan Creating a Factor. We use the factor () function to create factors. The following is the syntax of the factor () function: factor_name=factor (x=character (),levels,labels,exclude,ordered,nmax) Where x is a vector with the data for the factor, levels is an optional vector with unique values that x might take, labels is an optional vector of ...
Data Wrangling: De factores, levels and labels - R que R Levels: Vemos que R ha ordenado las distintas categorías según un criterio alfabético y, por ello, a la categoría alta le atribuye el número 1, a baja el número 2, a media el número 3, etc. El orden asignado por defecto podría ser funcional en el caso de variables de tipo nominal pero, sin embargo, existe un gran número de ocasiones en las que trabajemos con variables ordinales, como ... Quick-R: Value Labels To understand value labels in R, you need to understand the data structure factor. You can use the factor function to create your own value labels. # variable v1 is coded 1, 2 or 3 r - Changing factor levels with dplyr mutate - Stack Overflow Jan 28, 2015 · From my understanding, the currently accepted answer only changes the order of the factor levels, not the actual labels (i.e., how the levels of the factor are called). To illustrate the difference between levels and labels, consider the following example: R Factors and Factor Levels (With Examples) - DataMentor Following is an example of factor in R. > x [1] single married married single Levels: married single. Here, we can see that factor x has four elements and two levels. We can check if a variable is a factor or not using class () function. Similarly, levels of a factor can be checked using the levels () function.
Factor variables | R Learning Modules - University of California, … Factor variables. Version info: Code for this page was tested in R version 3.0.2 (2013-09-25) On: 2013-11-27 With: knitr 1.5 1. Creating factor variables. Factor variables are categorical variables that can be either numeric or string variables. There are a number of advantages to converting categorical variables to factor variables.
Get label for given level of factor in R - Stack Overflow Teams. Q&A for work. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. Learn more about Teams
FACTOR in R [CREATE, CHANGE LABELS and CONVERT data] - R CODER Mar 22, 2020 · The factor function. The factor function allows you to create factors in R. In the following block we show the arguments of the function with a summarized description. factor(x = character(), # Input vector data levels, # Input of unique x values (optional) labels = levels, # Output labels for the levels (optional) exclude = NA, # Values to be excluded from levels ordered = is.ordered(x ...
r - Confusion between factor levels and factor labels - Stack Overflow 3 Answers. Very short : levels are the input, labels are the output in the factor () function. A factor has only a level attribute, which is set by the labels argument in the factor () function. This is different from the concept of labels in statistical packages like SPSS, and can be confusing in the beginning.
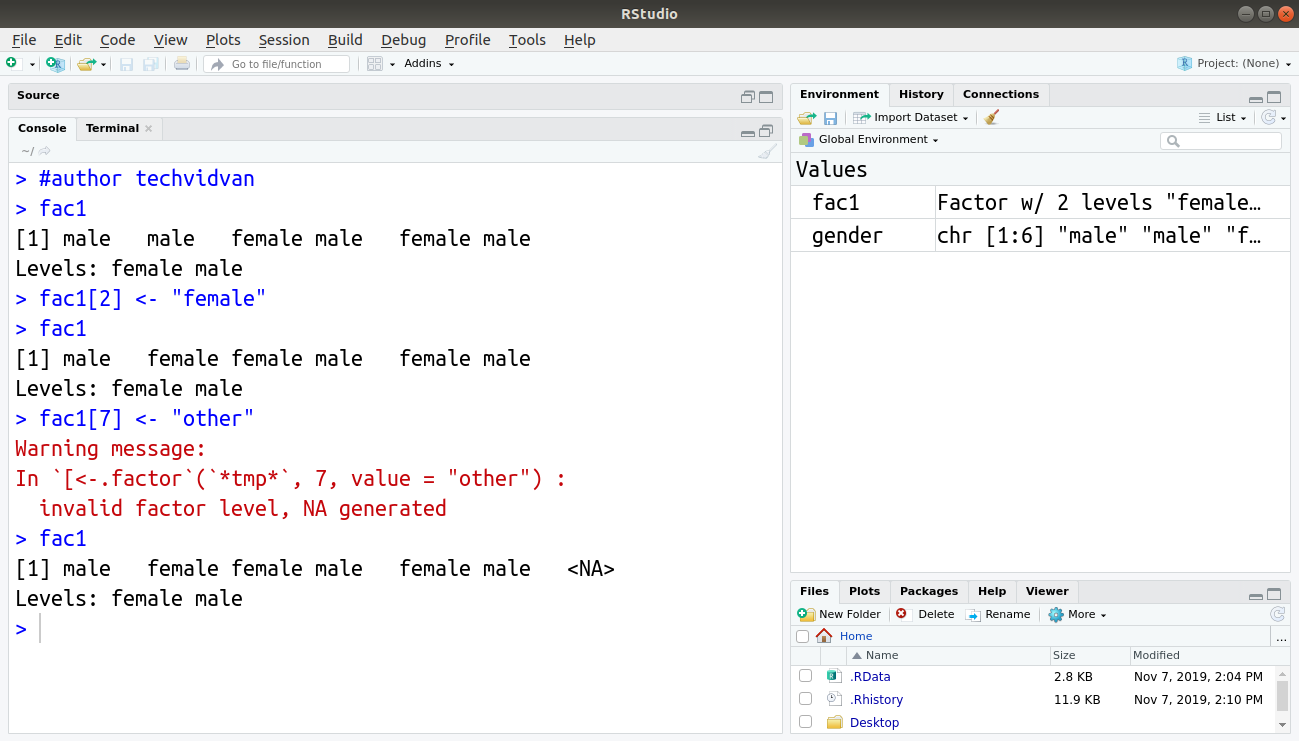
Too many factor levels to display in Regression Tree in R 0. I'm new to R and still figuring out the basics. I have a fairly large data set where some factors have many categories. How do I prevent R from including the labels in the tree image? The result is attached and is illegible. I'm using rpart.plot. Unfortunately, I may not reduce the number of categories. Otherwise, I would have. r.
How to label factors but still preserve its original levels' values - R The reason there are separate levels and labels arguments is because the vector you pass may not have every "level" in it. e.g. factor(1:3,levels = 1:4,labels = letters[2:5]).levels allows you to notify R that there are some categories you want "space" for that aren't in the original set, (also for ordering purposes).labels is just for choosing what to call those levels, rather than the ...
How to Rename Factor Levels in R (With Examples) - Statology How to Reorder Factor Levels in R. Published by Zach. View all posts by Zach Post navigation. Prev How to Calculate Cosine Similarity in Excel. Next How to Plot Multiple Histograms in R (With Examples) Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
An Introduction to R However in this simple instance (just one factor) what happens can be thought of as follows. The values in the vector are collected into groups corresponding to the distinct entries in the factor. The function is then applied to each of these groups individually. The value is a vector of function results, labelled by the levels attribute of the ...
Levels in R: What are the Factor Levels - R-Lang The levels () is an inbuilt R function that provides access to the levels attribute. The first form returns the value of the levels of its argument, and the second sets the attribute. You can assign the individual levels using the gl () function. When you first get a dataset, you will usually notice that it contains particular factor levels.
r - Why is the terminology of labels and levels in factors so weird ... Another way to think about levels is that factor(x,levels=L1,labels=L2) is equivalent to. f <- factor(x,levels=L1) levels(f) <- L2 I think an appropriately phrased version of this example might be nice for Pat Burns's R inferno-- there are plenty of factor puzzles in section 8.2, but not this particular one ...





![FACTOR in R ▷ [CREATE, CHANGE LABELS and CONVERT data]](https://r-coder.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Introduction-to-Statistical-Learning.png)




















Post a Comment for "41 r factor levels labels"